Osteoporosis
20/10/2021
Osteoporosis
Introduction:
Bones are the solid organs of which the human skeleton (skeletal system) is made up. Bones are in a constant state of renewal (remodeling). At early age, the bone tissue is produced (ossified) at a higher ratio than the breakdown (resorption) of old tissue—a process called bone ossification and resorption, bone remodeling, or bone metabolism. As people age, the metabolism process is reversed; such that resorption occurs at a higher ratio than ossification (which is typical of aging).
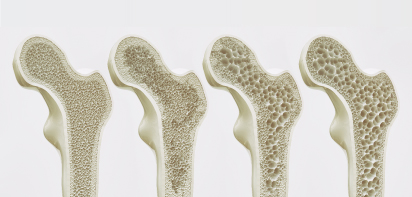
Osteoporosis:
Osteoporosis is a common health condition that weakens bones, making them fragile and more likely to break. It develops slowly over several years, and is often only diagnosed when a minor fall or sudden impact causes a bone fracture. Women are at higher risk of osteoporosis, especially post-menopause.
Other names of the disease:
Thinning bones, the silent disease.
Cause:
- Long-term use of some medications (such as taking corticosteroids or cortisone orally), and other medications such as heparin (an anticoagulant), as well as epilepsy medications (such as phenytoin);
- Some endocrine disorders such as: hyperactivity of the thyroid and parathyroid glands, Cushing's syndrome, and deficiency of estrogen;
- The density of women’s bones decreases dramatically in the few years post-menopause, particularly if the menopause begins early (before the age of 45).
Risk factors:
- Drinking alcohol, smoking and excessive caffeine use;
- Family history of osteoporosis-associated fractures;
- Deficiency of sex hormones (hypogonadism);
- Aging;
- Loss of weight;
- Deficiency of calcium or Vitamin D;
- Lack of physical activity.
Symptoms:
At early stages, osteoporosis does not usually cause any symptoms. As the diseases develops, though, the following symptoms may occur:
- Pain in the lower back (caused by braking or dislocation of a vertebra);
- Roundback (kyphosis), and getting shorter over time;
- Increased risk of fractures.
When to see a doctor?
- When getting old (+60 years old);
- After menopause, or undergoing an oophorectomy surgery;
- If you take cortisone for several months;
- If you take medications like cortisone, anticoagulant and epilepsy medications.
Complications:
- Fractures, particularly hip and spinal fractures:
They are the most serious bone fractures. Hip fractures are usually caused by falls. They may result in the patient’s paralysis, or even death, owing to the complications that may occur after surgeries, especially in the elderly.
Fractures of the spinal bones, or spinal fractures, may occur without injuries or falls. The weight pressure on the spinal bones (vertebrae) causes them to collapse on one another, causing a severe back pain.
- Multiple such spinal fractures may lead to the loss of some centimeters from the patient's height, and the appearance of roundback (kyphosis).
Diagnosis:
- Family history: examination of the risk factors (such as family history), symptoms and complications;
- Measuring how the bones are able to absorb X-ray, through DEXA scan, to measure the density of bones, especially the hip and spinal bones.
Treatment:
Following preventive precautions is necessary for the preservation of bone density, and hence avoid osteoporosis, in addition to avoiding falls and fractures. If a patient is diagnosed with osteoporosis, though, the physician shall determine the treatment method, based on the symptoms that the patient develops.
Prevention:
Prevention of osteoporosis should begin at an early age, through to all the subsequent age stages. Osteoporosis prevention depends on the following:
- A healthy diet: make sure that you get an adequate intake of proteins, calories, in addition to calcium and Vitamin D, all of which are necessary for preserving the bone formation and density;
- Calcium is necessary for all women post-menopause (the intake should not be less than 1000mg a day), whether from natural dietary sources, such as dairy products (milk, cheese, leben, etc.), and vegetables (turnip, broccoli, etc.), or by taking calcium supplements. The daily intake of calcium, however, should not be more than 2000mg, to avoid the calcium-associated side-effects;
- Vitamin D is also important for the bone health. Postmenopause women consume 800 IU of Vitamin D per day. Together with calcium, Vitamin D helps prevent osteoporosis-induced fractures in older women. Vitamin D is also found in milk, salmon fish, yogurt, orange juice and cereals. In case the daily intake of Vitamin D from natural dietary sources is insufficient, it should be taken—after consulting the doctor—as supplements;
- Quit smoking and stop drinking alcohol;
- Take regular exercise: exercising is an optimal way to preserve the bone density, strengthen muscles, preserve body balance, and, hence, reduce the risk of fractures;
- Avoid falls: falling increases the risk of fractures. To avoid falls:
- Remove robes and cables, as well as carpets, which may lead to stumbling and falling;
- Make sure to keep the house well-illuminated, including stairs and doorways;
- Avoid walking on slippery surfaces, such as: ice, and wet or slippery floor;
- Avoid waling in uneven areas; and
- See your doctor on a regular basis, to assess the visual acuity.
FAQ
- Can osteoporosis be detected early in women?
Most women are examined for osteoporosis when they are 65 years old. They can be screened before 65, after menopause, or in case they are at risk of osteoporosis (for example, smoking). The osteoporosis examination is conducted through clinical examination, medical history, and measurement of the bone density.
References:
Saudi Ministry of Health